| Ãðóïïà áèîôèçèêè |
(English version only)
(formerly led by Prof. Vladimir VOROBYEV, ceased in 2009)

Alexey SKVORTSOV
|

Alexander POLYANICHKO
|

Elena CHIKHIRZHINA
|

Elena KOSTYLEVA
|

Natalia SERGEEVA
|
|
RESEARCH TOPICS
Molecular mechanisms of primary events in platinum drug metabolism
Dr. Alexey SKVORTSOV
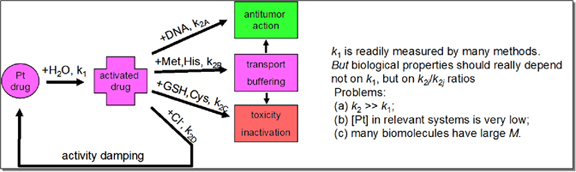
Platinum cytostatic agents are a class of extensively studied DNA-damaging compounds which includes potent platinum antitumour drugs (cisplatin, carboplatin and oxaliplatin).
Biological activities (antitumor properties, tissue-specific cell resistance, general and specific toxicities) depend strongly structure of coordination sphere of platinum drug. Yet the
relationship between structure and activity for platinum drugs is still poorly understood, and many controversies exist concerning the biological role of reactions of platinum drugs with
non-DNA targets.
Dr. Alexey SKVORTSOV
One of the main obstacles in studying reactions of platinum complexes in biologically relevant conditions (submicromolar concentrations of platinum) is the absence
of characteristic properties in platinum drugs, which limits the number of available techniques. Optical absorption spectroscopy in UV-bands of platinum drugs offers good sensitivity,
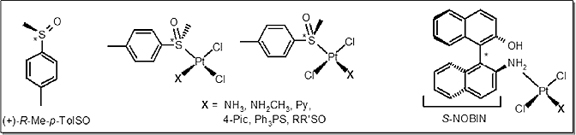
but it has obvious limitation, as most biomolecules also absorb in UV region. One of the solutions, proposed earlier by our group was the usage of optically active platinum complexes
with strong stereogenic centers, which are close structural analogs of platinum drugs. Strong circular dichroism (CD) bands of such ligands, which are easily tractable serve as a
'chiral label' for reaction studies.
Financial Support: RFBR-BRFBR grant 10-04-90048-Bel; President grant MK-5692.2008.4
Publications
Skvortsov A.N., Uvarov V. M., de Vekki D. A., Studentsov E. P., Skvortsov N. K. (2010) Conformational Analysis, Spectral and Catalytic Properties of 1,3-Thiazolidines,
Ligands for Acetophenone Hydrosilylation with Diphenylsilane // J. Gen. Chem. Rus. 80 (10): 2007-2021.
Skvortsov A.N., Spevak V. N., Studentsov E.P., Sokolova O.V., Skvortsov N.K. (2010) Synthesis and Spectral Properties of Mixed-Ligand Platinum(II) Complexes
with (-)-S-NOBIN and Sulfoxides // J. Gen. Chem. Rus. 80 (10): 1963-1971.
Studentsov E. P., Piskunova O. V., Skvortsov A.N., Skvortsov N.K. (2009) Synthesis and Optical Properties of (S)-Nobin // J. Gen. Chem. Rus. 79 (3): 962-965.
Bachurina I.V., Skvortsov A.N., Skvortsov N.K., Il'yushin M.A. (2009) Synthesis and Spectral Characteristics of the Combined Ligand Copper Complex with Proline and
Corazole // J. Gen. Chem. Rus. 79 (3): 505-508.
Skvortsov A.N. 2009 [Efficient method of analysis of optical spectra from kinetic studies]. // Tsitologyia. 51 (3): 229-239 (in Russian).
Fridman A.S., Galyuk E.N., Vorob'ev V.I., Skvortsov A.N., Lando D.Y. (2008) Melting of crosslinked DNA: VI. Comparison of influence of interstrand crosslinks and other
chemical modifications formed by antitumor compounds on DNA stability. // J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 26 (2): 175-185.
Skvortsov A.N., Reznikov A.N., de Vekki D.A., Stash A.I., Belsky V.K., Spevak V.N., Skvortsov N.K. (2006) Synthesis and crystal structures of platinum (II) complexes
with phosphine sulfide: cis-Dichloro [dimethylsulfoxide] (triphenylphosphine sulfide) platinum (II) and (–)-cis-dichloro[(S)-methyl-p-tolylsulfoxide]
(triphenylphosphine sulfide) platinum (II). // Inorganica Chimica Acta 359 (4): 1031-1040.
Skvortsov A.N., de Vekki D.A., Stash A.I., Belsky V.K., Spevak V.N., Skvortsov N.K. (2002) Synthesis, crystal structures and optical activity of cis- and
trans-(–)-dichloro[(S)-methyl p-tolylsulfoxide]pyridyl platinum(II) complexes. // Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 13 (15): 1663-1671.
Elena SKVORTSOVA, Dr. Alexey SKVORTSOV
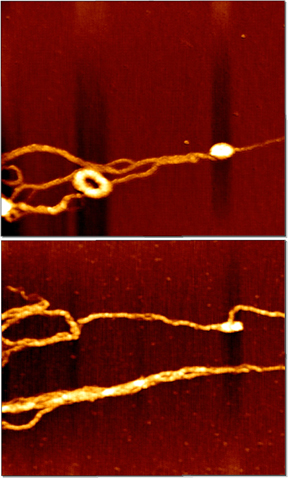
Transfection of cells is a very important step in genetic engineering of eukaryotic cells, both in research and therapy applications. Efficient DNA carriers should be
biocompatible, bind DNA reversibly, protect it in extracellular environment and target it to cell nucleus. For therapy applications the carriers should also be non-toxic and degradable.
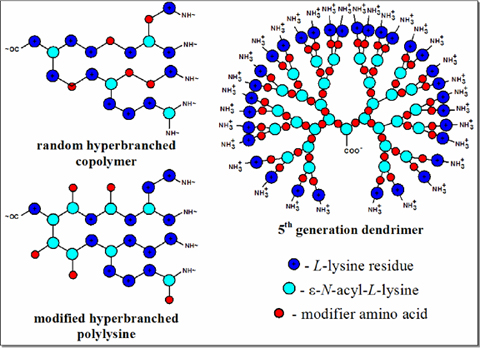
Polycationic branched polymers of L-lysine and its copolymers with other amino acids are a promising group of DNA carriers.
Publications
Vlasov G.P., Filippov A.P., Tarasenko I.I., Tarabukina E.B., Pankova G.A., Il'ina I.E., Shpyrkov A.A., Skvortsova E.V., Skvortsov A.N., and Vorob'ev V.I. (2008) Hyperbranched
Poly(L-lysine) Modified with Histidine Residues via Lysine Terminal Amino Groups: Synthesis and Structure // Polymer Science, Series A. Polymer Physics 50 (4): 374-381.
Vlasov G.P., Tarasenko I.I., Valueva S.V., Kipper A.I., Tarabukina E.B., Filippov A.P., Avdeeva (Skvortsova) E.V., and Vorob'ev V.I. (2005) Hyperbranched Poly(L-lysine)
Containing Additional Amino Acids or Their Oligomers Between Branching Points: Synthesis and Structure // Polymer Science, Series A. Polymer Physics 47 (5): 422-429.
Guryanov I.A., Vlasov G.P., Lesina E.A., Kiselev A.V., Baranov V.S., Avdeeva (Skvortsova) E.V., and Vorob'ev V. I. (2005) Cationic Oligopeptides Modified with Lipophilic
Fragments: Use for DNA Delivery to Cells // Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry 31 (1): 18-26.
Shpakov A.O., Gur'ianov I.A., Avdeeva (Skvortsova) E.V., Vorob'ev V.I., Vlasov G.P. [Molecular mechanisms of action of dendrons, containing 48-60 sequence of HIV-1
TAT-protein, on the functional activity of the adenylyl cyclase signaling systems]. // Tsitologiya 46 (11): 1011-1022, in Russian.
Dr. Alexander POLYANICHKO, Dr. Elena CHIKHIRZHINA, Tatyana RODIONOVA, Elena KOSTYLEVA
Structural organization of DNA in chromatin has been extensively studied for many years. When the structure of the nucleosome
was solved, the investigations of the higher levels of the structural organization became one of the most important steps in understanding the functioning of chromatin. A great variety
of DNA-binding proteins interact with DNA forming intricate protein-DNA complexes. DNA-bound protein factors normally cooperate to assemble higher-order nucleoprotein structures
in which multiple protein-DNA and protein-protein contacts increase the specificity and stability of the final complexes. Interactions between proteins bound to neighboring regulatory
elements allow cooperative DNA binding without encountering any serious topological difficulties. However, interactions between DNA-bound proteins that are not directly adjacent
require a deformation of the DNA double helix, which is energetically unfavorable for DNA fragments shorter than ~140 nucleotides. Binding of 'architectural' proteins can nonetheless
change the situation. Among such proteins, HMGB-domain proteins are particularly intriguing.
Structural aspects of antitumor activity of platinum coordination compounds.
Our studies are aimed at the investigation of structure-to-function correlations for DNA-protein complexes of chromatin, using the
variety of physical-chemical approaches, including:
Publications
Tsankov D., Polyanichko A., Wieser H. (2010) Vibrational Circular Dichroism: Ensuring Quality of Pharmaceutical Products, In: "Handbook of Analysis and Pharmaceutical Quality.
Pharmaceutical Sciences Encyclopedia: Drug Discovery, Development, and Manufacturing", Edited by Shayne C. Gad, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1-41. (Online ISBN: 978-0-4705-7122-4).
Polyanichko A.M., Andrushchenko V.V., Bour P., Wieser H. (2011) Vibrational circular dichroism studies of biological macromolecules and their complexes. Chapter 2. In:
"Circular Dichroism: Theory and Spectroscopy", Edited by David S. Rodgers, Nova Science Publishers, Inc., New York, USA, 2011, 61 pp. (ISBN: 978-1-61122-522-8).
Polyanichko A. and Wieser H. (2010) Structural organization of DNA-protein complexes of chromatin studied by vibrational and electronic circular dichroism. Spectroscopy:
An International Journal, 24 (3-4), 239-244.
Chikhirzhina E., Polyanichko A., Leonenko Z., Wieser H., Vorob'ev V. (2010) C-terminal domain of nonhistone protein HMGB1 as a modulator of HMGB1-DNA structural interactions.
Spectroscopy: An International Journal, 24 (3-4), 361-366.
Rodionova, T.Y., Chikhirzhina, E.V., Vorob'yov, V.I., Polyanichko, A.M. (2010) Changes in the secondary structure of HMGB1 protein bonded to DNA. Journal of Structural
Chemistry 50 (5), 976-981.
Polyanichko, A. M., Leonenko, Z. V., Cramb, D., Wieser, H., Vorob'ev, V. I., & Chikhirzhina, E. V. (2008). Visualization of DNA complexes with HMGB1 and its C-truncated
form HMGB1(A+B). Biophysics 53 (3), 202-206.
Polyanichko, A. M., Chikhirzhina, E. V., Andrushchenko, V. V., Vorob'ev, V. I., & Wieser, H. (2006). The effect of manganese(II) on the structure of DNA/HMGB1/H1 complexes:
Electronic and vibrational circular dichroism studies. Biopolymers 83 (2), 182-192.
Polyanichko, A. M., Chikhirzhina, E. V., Andrushchenko, V. V., Wieser, H., & Vorob'ev, V. I. (2005). Spectroscopic investigations of the structure of DNA complexes with mn
2+ in UV and IR regions. Biophysics 50 (5), 710-715.
Polyanichko, A., & Wieser, H. (2005). Fourier transform infrared/vibrational circular dichroism spectroscopy as an informative tool for the investigation of large supramolecular complexes of biological macromolecules. Biopolymers 78(6), 329-339.
Polyanichko, A. M., Chikhirzhina, E. V., Andrushchenko, V. V., Kostyleva, E. I., Wieser, H., & Vorob'ev, V. I. (2004). The effect of Ca2+ ions on DNA compaction in the
complex with non-histone chromosomal protein HMGB1. Molecular Biology 38 (4), 701-712.
Polyanichko, A. M., Chikhirzhina, E. V., Kostyleva, E. I., & Vorob'ev, V. I. (2004). Structure of DNA complexes with nonhistone chromosomal protein HMGB1 in the presence of
manganese ions. Molecular Biology 38 (6), 891-898.
Polyanichko, A. M., Andrushchenko, V. V., Chikhirzhina, E. V., Vorob'ev, V. I., & Wieser, H. (2004). The effect of manganese(II) on DNA structure: Electronic and
vibrational circular dichroism studies. Nucleic Acids Research 32 (3), 989-996.
Polyanichko, A. M., Chikhirzhina, E. V., Andrushchenko, V. V., Kostyleva, E. I., Wieser, H., & Vorob'ev, V. I. (2004). The effect of Ca2+ ions on DNA
compaction in the complex with HMGB1 nonhistone chromosomal protein. Molecular Biology 38 (4), 590-599.
Chikhirzhina, E. V., Polyanichko, A. M., Skvortsov, A. N., Kostyleva, E. I., Houssier, C., & Vorob'ev, V. I. (2002). HMG1 domains: The victims of the circumstances.
Molecular Biology 36 (3), 412-418.
Polyanichko, A. M., Chikhirzhina, E. V., Skvortsov, A. N., Kostyleva, E. I., Colson, P., Houssier, C., et al. (2002). The HMG1 ta(i)le. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and
Dynamics 19 (6), 1053-1062.
Polyanichko, A. M., Davydenko, S. G., Chikhirzhina, E. V., & Vorob'ev, V. I. (2000). The interaction of supercoiled DNA with nonhistone protein HMG1.
Tsitologiya 42 (8), 792-793.
Dr. Vanda M. SEDOVA
We have developed macro and micro methods to isolate DNA- dependent RNA polymerase III of human placenta nuclei and human epidermoid carcinoma cells A431.
RNA polymerase III have been isolated by both methods as two subfractions, IIIa and IIIb, with different buoyant density in gradient of glycerol concentration. Protein kinase activity,
phosphorylating in vitro six joint subunits of both subfractions , and two subunits with molecular weight about 30 and 93 kDa of subfraction IIIa and subunit with molecular weight about 95 kDa
of -IIIb is co-purified with both RNA polymerase III subfractions. This protein kinase activity was not identified in cells A431 after 48 hours long starvation. The subunit of IIIa subfraction with
molecular weigt about 95 kDa is phosphorylated on phophotyrosine as identified by immunoblotting with antibodies against phosphotyrosine, the same subunit of IIIb subfraction is
phosphorylated on tyrosine residues not in each enzyme preparation. At least four subunits with molecular weight 90 kDa and lower of the both subfractions of RNA polymerase III of human
placenta nuclei are phosporylated in vivo as it has been shown by INDIA Phosphoprobe Kit for phosphorylated polypeptides identificating method. The phosphorylation of RNA polymerase IIIa
of human placenta nuclei in vitro causes the activation of specific Alu-repeat, tRNAiMet1 and 5S rRNA genes consisting templates. Transcription activation depends on the presence or absense
of specic template during phosphorylation of the enzyme in vitro. The subfractions of RNA polymerase of human placenta nuclei don't include protein phosphotase activity. The co-purified protein
kinase utilases ATP and GTP as donors of phophate groups. Dephosphorylation of RNA polymerase IIIa of human placenta nuclei by immobilezed alkaline phosphotase in vitro causes inhibition
of Alu- template transcription, dephosphorylated RNA polymerase cann't be substrate of phosphorylation by co-pyrified protein kinase. It may be the copyrified protein kinase losts enzymatic
activity through dephosphorylation. Co-pyrified protein kinase aren't numbered to MAP-kinase family as it has been shown by immunobloting method with antibody against MAP-kinase.
Two subunits with molecular weight about 200 kDa and 75 kDa were identified in RNA polymerase IIIa and IIIb subfractions of human placenta nuclei by immunobloting method with antibody
against TOR- kinase. It is possible that co- pyrified protein kinase, phosphorylating RNA Polymerase III in vitro, belongs to inosytol 3-kinase (PI3- kinase) family thus its activity is inhibited by
vortmanin - specific inhibitor of PI3 kinase. The levels of 5S rRNA, initiator tRNAiMet1 and Alu-gene expression in human epidermoid carcinoma cells A431 being in different physiological states
upon growing in serum-free media causes the prolongation of generation period, activated to proliferation by low concentration of epidermoid growth factor (EGF) - 0.1 ng/ml, and high
concentrations of EGF - 10-100 ng/ml, cause apoptosis. were investigated by real-time RT-PCR method. It was showed that studied Alu-repeat wasn't expressed in cells A431. The level of
initiator tRNAiMet1 in actively proliferating cells was 1.7 times higher than in slowly proliferating cells and was remained just high in apoptotic cells. The proportion of 5S rRNA was practically
the same in slowly and actively proliferating A431 cells, and was increased about 2.5-fold in apoptotic cells.
Boris V. SHESTOPALOV
The underlying task of investigations is solution of the major problem of fundamental science of paramount significance - creation of the
code-based protein physics as a part of the new section of theoretical physics which is destined for description of systems consisted of numerous different elements, connected
together. The immediate task of investigations is to develop the algorithm of formation of the three-dimensional structure of water-soluble proteins when an amino acid sequence is
given using computer simulation and obtained previously results of simulation of formation of alpha-helices and beta-strands which are supported by experimental data.
Additional info: http://www.cytspb.rssi.ru/persons/shestopalov/shestopalov_en1.pdf
Publications
Shestopalov B.V. (2007) The code-based physics of formation of a-helices and b-hairpins in water-soluble proteins. Doklady Biochemistry and Biophysics.
Vol. 416, pp 245-247.
Shestopalov B.V. (2007) Simulation of formation of a-helices and b-hairpins in water-soluble proteins by the code-based physics. Cell and Tissue Biology.
Vol. 1, No. 5, pp. 420-426.
Shestopalov B.V. and G. R. Mavropulo-Stolyarenko (2007) The most complete list of unique protein structures solved by x-ray crystallography. Molecular Biology.
Vol. 41, No. 4, pp. 680-681.
Shestopalov B.V. (2005) Comparison of x-ray diffraction analysis and nuclear magnetic resonance from data on the identification of a-helices and b-strands in the same protein.
Biophysics. Vol. 50, No. 6, pp. 862-864.
Shestopalov B.V. (2003) Amino acid code of protein secondary structure. Tsitologiya. Vol. 45, No. 7, pp. 702-706.
Shestopalov B.V. (2003) Statistical model of amino acid code of protein secondary structure. Tsitologiya. Vol. 45, No. 7, pp. 707-713.
Kouprina N., Kirillov A., Kroll E., Koryabin M., Shestopalov B., Bannikov V, Zakharyev V, Larionov V. (1993) Identification and cloning of the CHL4 gene controlling chromosome
segregation in yeast. Genetics. Vol. 135, ¹ 2, pp 327 - 341.
Kouprina N., Kroll E., Bannikov V., Bliskovsky V., Gizatullin R., Kirillov A., Shestopalov B., Zakharyev V., Hieter P., Spencer F., Larionov V. (1992) CTF4 (CHL15) mutants exhibit
defective DNA metabolism in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. Vol. 12, ¹ 12, pp 5736 - 5747.
Shestopalov B.V. (1988) Amino acid sequence template useful for helix-turn-helix prediction. FEBS Lett. Vol. 233, pp. 105-108.
Gultyaev A.P., Shestopalov B.V. (1988) Structural basis for autogenous regulation of Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein L1 synthesis at the splicing level. FEBS Lett.
Vol. 232, ¹ 1, pp 9 - 11.
Shestopalov B.V., Chirgadze Yu.N. (1976) Quantitative study of secondary structure of histones H1, H2A, and H4 in solution by infrared spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem.
Vol. 67, ¹ 1, pp 123 - 128.
Chirgadze Yu.N., Shestopalov B.V., Venyaminov S.Yu. (1973) Intensities and other spectral parameters of infrared amide bands of polypeptides in the b- and random forms.
Biopolymers. Vol. 12. ¹ 6. pp 1337 - 1351.
|
-
⇑
Beginning
| Íàó÷íûå ïîäðàçäåëåíèÿ | Ãëàâíàÿ | |